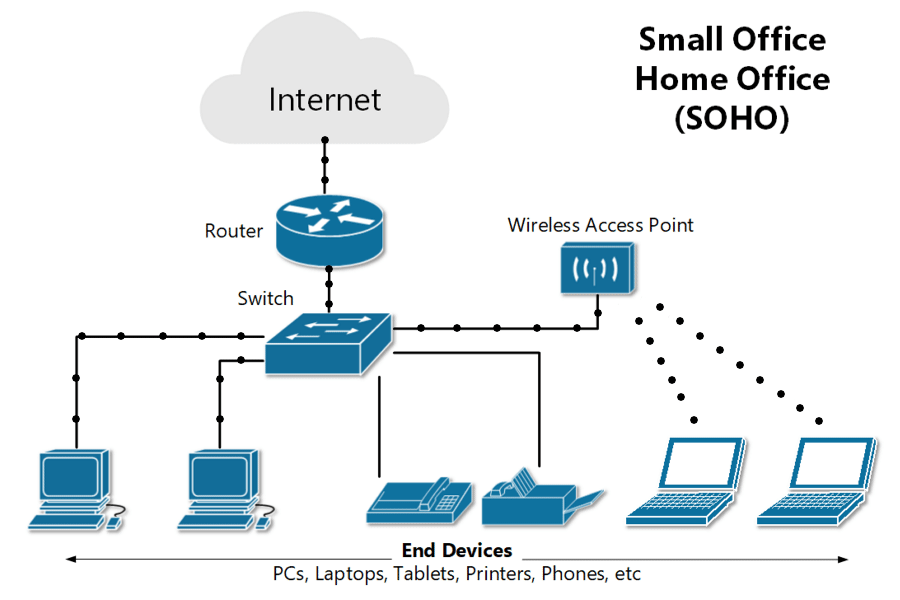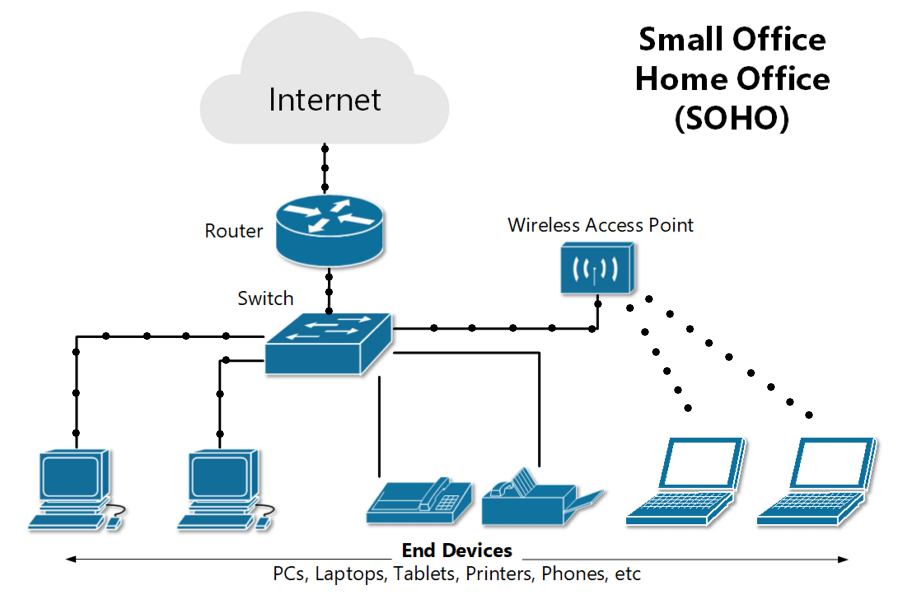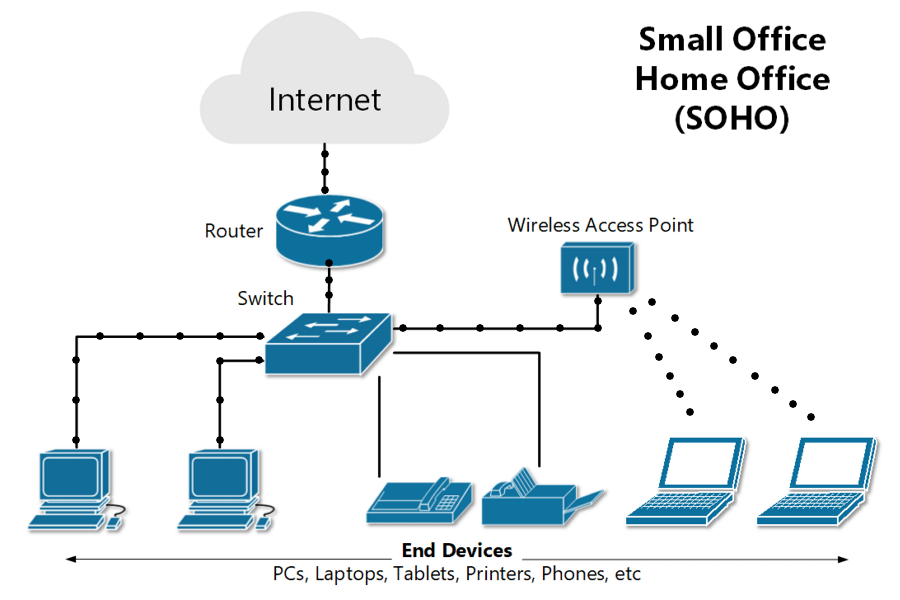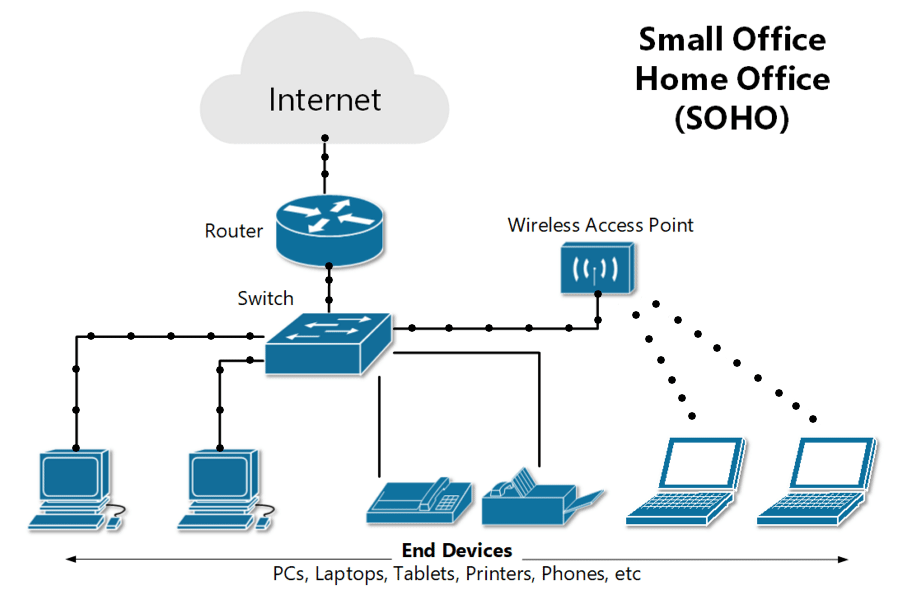
Setting up a small office computer network involves careful planning to ensure security, reliability, and scalability for future growth. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you set up a basic wired and wireless network for a small office:
-
Assess Your Needs:
- Determine the number of computers, printers, and other devices that will be connected.
- Estimate the amount of data traffic and bandwidth required.
- Consider any specialized software or applications the business may use.
-
Obtain Necessary Hardware:
- Router: This is the heart of your network. For a small office, consider a router that provides both wired (Ethernet) and wireless (Wi-Fi) connectivity.
- Switch: If you have more wired devices than your router can accommodate, get an Ethernet switch.
- Modem: If not provided by your ISP, you’ll need a modem to connect to the internet.
- Cabling: Purchase Ethernet cables (CAT5e or CAT6) for wired connections.
- Wireless Access Points (WAP): If your office is large, you might need additional WAPs to ensure full wireless coverage.
-
Setup Internet Connectivity:
- Connect the modem to the incoming internet line (this could be DSL, cable, fiber-optic, etc.)
- Connect the router to the modem using an Ethernet cable.
- Turn on the modem first, wait for a minute, then turn on the router.
-
Configure the Router:
- Connect a computer to the router using an Ethernet cable or Wi-Fi.
- Access the router’s web interface by typing its IP address into a web browser (common addresses include 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1).
- Login using the default credentials (usually “admin”/”admin” or indicated at the bottom of the router).
- Change the default login credentials to ensure security.
- Set up Wi-Fi by choosing a strong SSID (network name) and setting a robust password. Opt for WPA3 encryption if available.
- Disable WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) as it can be a security vulnerability.
- Update the router’s firmware to the latest version for optimal performance and security.
-
Connect and Set Up Devices:
- Connect computers and other devices to the network, either wired or wirelessly.
- Set up shared resources, like network printers or storage.
-
Implement Security Measures:
- Firewall: Ensure the router’s built-in firewall is enabled.
- VPN: If remote access is needed, consider setting up a VPN for secure external connections.
- Guest Network: If visitors or clients need internet access, set up a guest network separate from your main network.
- Antivirus/Antimalware: Ensure all devices have up-to-date security software.
- Regular Backups: Set up regular backups for critical data.
-
Regular Maintenance:
- Periodically check for and install firmware updates for your router and other network equipment.
- Monitor data usage and network performance.
- Regularly review and update security protocols.
-
Plan for Growth:
- As your business grows, you might need more bandwidth, additional networking equipment, or advanced features like VLANs. Periodically reassess your network setup to ensure it aligns with your business needs.
Here are some additional tips for setting up a small office computer network:
- Use a managed switch. A managed switch allows you to configure more advanced features, such as port security and VLANs.
- Use a firewall. A firewall can help protect your network from unauthorized access.
- Use antivirus software. Antivirus software can help protect your network from malware.
- Keep your software up to date. Software updates often include security patches that can help protect your network from vulnerabilities.
- Train your employees on cybersecurity best practices. Employees should be aware of the risks of cybersecurity threats and how to protect themselves.
By following these steps, you can set up a small office computer network that is reliable, secure, and easy to manage.
Here are some of the most common types of networks used in small offices:
- Ethernet: Ethernet is the most common type of network used in small offices. It uses cables to connect devices together.
Ethernet network
- Wireless: Wireless networks are becoming increasingly popular in small offices. They allow devices to connect to the network without the need for cables.
Wireless network
- Fiber optic: Fiber optic networks are a more expensive option, but they offer faster speeds and better security than Ethernet or wireless networks.
Fiber optic network
- VPN: A virtual private network (VPN) is a secure way to connect to a remote network. This can be useful for small offices that need to connect to a corporate network or to access files and applications that are not available on the local network.
VPN network
The best type of network for your small office will depend on your needs and budget. If you are not sure which type of network is right for you, you should consult with a MDofPC Doctor of Computers network engineer or IT professional.
